Introduction
Private equity has a significant influence on financial markets, presenting investors with opportunities distinct from public equities. Therefore, recognizing the concept of private equity investment is essential, especially for investors who aim for a higher return and diversification of their portfolio. This article will help demystify the issues related to Private equity investment, explaining how investors can get these opportunities and how they can more effectively apply private equity investment strategies. Through this approach, we aim to increase understanding of private equity and, therefore, its popularity among potential investors.
The Basics of Private Equity
Private equity is the process of acquiring and restructuring firms that are not listed on the stock exchange market. Private equity and venture capital firms often provide the necessary funds, with the aim of enhancing the company’s value, typically investing to improve the business and later selling their stake for a profit. To get a clearer perspective of private equity investment, it is crucial to look at its basic conceptualization.
Key elements of private equity:
-
General Partners (GPs): Have control of the fund, they make decisions on who to invest in or where to invest the funds and are also held accountable for the results.
-
Limited Partners (LPs): The majority of the capital, including pension funds, endowments, and other high-net individuals, are expected to be the major source.
Private equity investments can take various forms, including:
-
Venture Capital: It is mainly directed towards dynamic start-ups with high growth capabilities. It entails making money deposits that offer early-stage firms and businesses capital that they otherwise cannot secure in conventional financial markets.
-
Growth Capital: Banks fund primarily business organizations that need the capital necessary for growth or perhaps a restructuring of business activities. Such capital aids organizations in enhancing their growth patterns and market standings.
-
Buyouts: Often implies the acquisition of a large block of a firm using cash and lots of debt. Acquisitions sometimes incorporate changes in the organizational framework to increase operational effectiveness and revenues.
Thus, the private equity market works as an essential part of the financial system and contributes its expertise and access to various sectors.
The Appeal of Private Equity Investments
Private equity investments have attracted much attention owing to their qualitative benefits and high-value creation. Private equity tends to have a greater level of involvement with the companies the funds target for investment which can lead to a better chance of yielding better returns than other public market investments. Thereby resulting in the diversification of the portfolio.
Here are some of the key appeals:
-
Higher Returns Potential: Traditionally, private equity investments yield greater returns than public markets, giving the investors a chance at getting higher returns. It is done by developing and implementing management and operating strategies in the portfolio companies.
-
Diversification Benefits: Private equity investments allow balancing the investors’ investment portfolios. With the help of private equity, investors can diversify to invest in different classes of instruments and sectors, thus lowering risks in the fluctuating market.
-
Active Management and Value Creation: Private equity firms are very much involved in the management and operation of their invested portfolio companies. This kind of experience results in improving operational synergies, as well as strategic development and growth plans, consequently enhancing the worth of the organization. The existence of private equity firms to investors adds a lot of benefits in terms of expertise and resources that would otherwise be unavailable to them.
All these reasons make private equity investments good investment opportunities in an investment portfolio— a way of investing in high-return, diversified, and actively managed investments.
Entry Points into Private Equity Investment
It is possible to get access to private equity investment in the following ways that also have their special features. Such points of entry are important for investors seeking to broaden their scope and harness the potential of private equity investments.
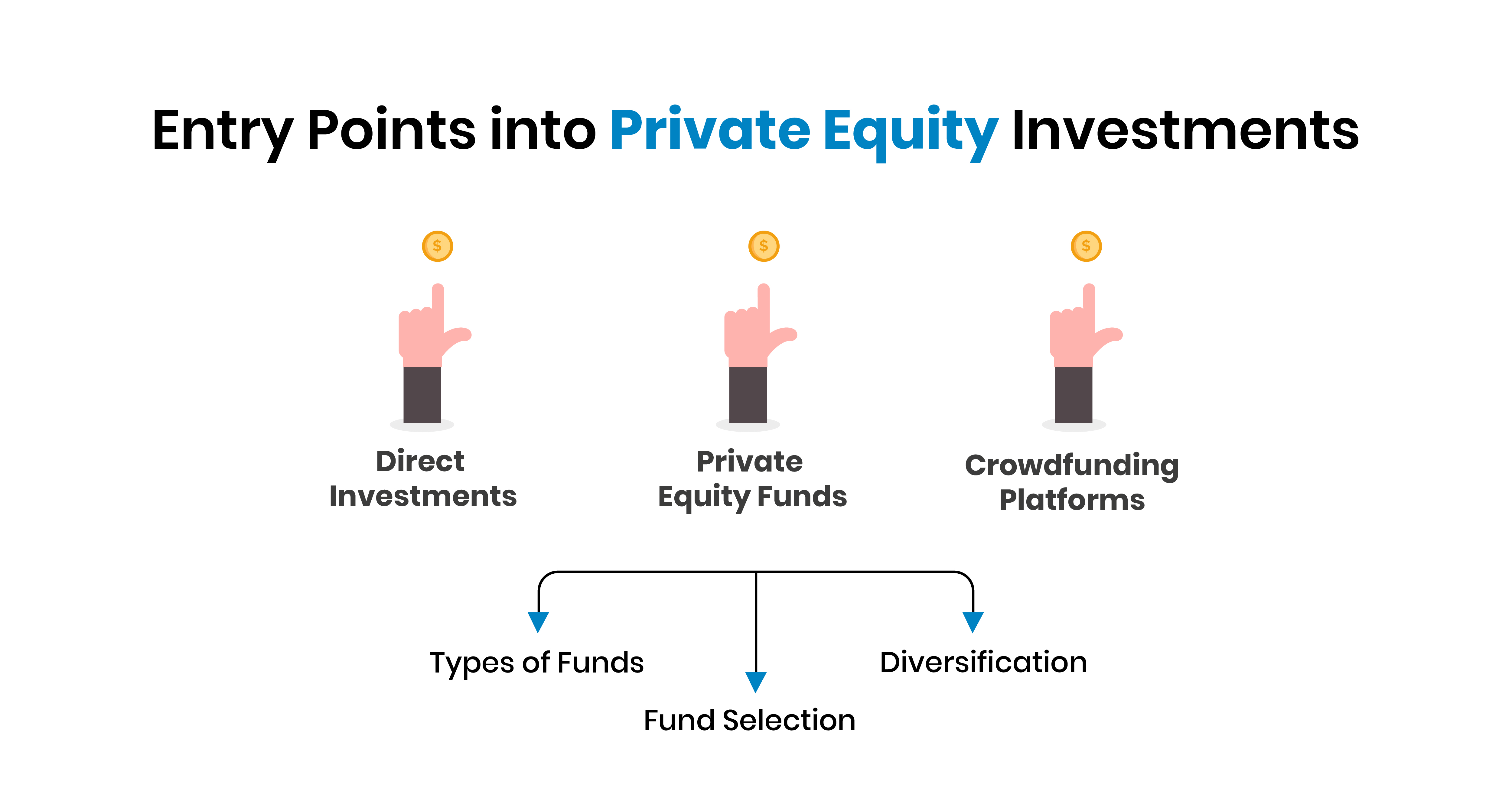
-
Direct Investments
These include investments where the fund invests directly in private companies or enterprises. Promoting this approach means that investors can have overall control and extensive participation in the management of the company. But it demands more cash, ample research, and better insights into the targeted sector or market.
-
Private Equity Funds
Management by professionals and diversification through private equity fund structure remain one of the main ways of participating in the investing process. These funds collect money from different investors to invest in various private companies. Key considerations include:
- Types of Funds: These are the buyout funds, venture capital funds, and growth equity funds with varying risk-adjusted returns.
- Fund Selection: Assess its historical performance, portfolio managers, investment approach, and fees and expenses.
- Diversification: Continuing one’s investments into a fund of funds can help diversify the pool of investments across several private equity funds.
-
Crowdfunding Platforms
Private equity investment has reached citizens through online crowdfunding sources. Such platforms allow the investor with less capital to be able to invest in private equity with relatively low amounts of money. It provides higher access, though one should consider a platform’s reputation, quality of the posted offerings, and risks.
Entering private equity can be beneficial and risky at the same time, so it is crucial to choose the one depending on the investor’s goals and preferences.
Exploring Private Equity Investment Platforms
Private equity platforms have emerged as an important way of unlocking private equity investment opportunities for a wider population of investors. These platforms act more as brokers who help direct investors to potential private equity investments, which are usually difficult to access due to high entry barriers.
Popular Platforms
-
AngelList: A platform, like LinkedIn for professional networking, AngelList is a popular website that was founded to provide funding to startup businesses.
-
SeedInvest: This strategy of financing is based on equity where funds are raised by employing the sale of shares on this platform to invest in promising startups.
-
CrowdStreet: Focused mainly on corporate real estate investment deals and provides access to the finest real estate opportunities.
Advantages of Private Equity Platforms
-
Lower Investment Minimums: Motivated by the success of private equity funds, these platforms do not necessarily involve significant amounts of money for investment; they can practically attract individual investors due to their lower expected investment minimums.
-
Transparency: Extensive information regarding each investment opportunity, including financials, management teams, and market prospects, is easily accessible, which helps investors make informed decisions.
-
Diversification: The investors can diversify their capital, and hence the risks of each deal in the portfolio are minimized.
Considerations
-
Due Diligence: While there is a lot of information available on different platforms, it is still necessary to do proper research on particular platforms. Check the platform’s performance, the quality of listed deals, and the possible fees.
-
Liquidity: Such investments can therefore lock funds for a longer time than it is possible for stocks bought through these platforms, and so there is low liquidity.
The main challenge in managing private equity platforms is to find the right approach that enables easy access while ensuring adequate research has been conducted to harness the full benefits of private equity investment.
Core Private Equity Investment Strategies
Private equity provides several approaches that depend on the level of risk tolerance and investment goals. These strategies are core components of how funds raise and invest capital and facilitate returns, with the help of active management and value creation. Here's an exploration of some core strategies:
-
Buyouts and Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs): These are characterized by the use of a large percentage of debt to achieve a controlling interest in a firm. LBOs intend to increase operating efficiency, decrease expenses, and increase rates of return before the firm’s divestment through sales or an initial public offering.
-
Venture Capital: This specializes in growth capital or providing funds to early-stage or startup firms. Venture capitalists not only give money, but also involve guidance to help these companies grow in different phases.
-
Growth Equity: Designed for mature business organizations that are about to embark on rapid growth, growth equity investments fund scaling operations, new market expansion, or organizational restructuring to facilitate faster growth. But notably, they do not include high-risk profiles of startups.
-
Distressed Assets and Special Situations: This involves the provision of capital to companies or other situations that would benefit from the infusion of funds and need financial help. Such investments focus on restructuring opportunities, operating enhancements, or divestitures to create value.
These strategies demonstrate the various techniques that private equity firms use in the generation of returns and managerial risks, depending on the market conditions. All of them entail responsible research, active management, and the comprehension of the sector specifics to achieve success for both investors and portfolio management companies.
Conclusion
Opportunities of private equity investment led to openings for diversified investment portfolios, possible high return on investment, and direct participation in business management. This implies learning to tackle risks with proprietary investing techniques, leveraging on trends such as digitalization, as well as an internationalist perspective on investment. As this sector is still developing, accepting its probability is not only a guarantee of financial improvement but also an opportunity to contribute to the formation of a stable, proactive, and innovative investment strategy in the future.








